Positive Feedback Loop of Long Noncoding RNA OASL-IT1 and Innate Immune Response Restricts the Replication of Zika Virus in Epithelial A549 Cells
- PMID: 33626545
- PMCID: PMC8138224
- DOI: 10.1159/000513606
Positive Feedback Loop of Long Noncoding RNA OASL-IT1 and Innate Immune Response Restricts the Replication of Zika Virus in Epithelial A549 Cells
Abstract
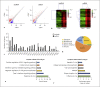
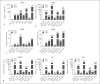
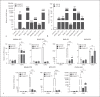
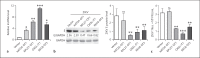
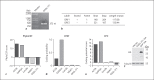
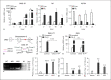
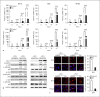
Expression of host noncoding RNAs and coding mRNAs is significantly altered by viral infection. In the current study, we screened the transcriptional profile of human lung epithelial A549 cells infected with Zika virus (ZIKV) by microarray assay. Seventy-nine long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and 140 mRNAs were differentially expressed (DE). The bioinformatics analysis revealed that the mRNAs adjacent to the DE lncRNAs were closely related to the host responses to viral infection. We selected 7 lncRNAs from the top 50 hits for validation. The quantitative real-time PCR data confirmed that expression of selected lncRNAs was induced by ZIKV infection. Moreover, the expression of 7 lncRNAs was induced by infection of dengue virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, or vesicular stomatitis virus, or by treatment of poly(I:C) and IFN-β. Furthermore, loss of innate immune adaptor IPS-1 or receptor IFNAR1 resulted in lower induction levels of several lncRNAs by ZIKV. Overexpression of 3 lncRNAs (RPL27-OT1, OASL-IT1, and REC8-OT3) reduced the virus yields of ZIKV. Knockout of OASL-IT1 significantly enhanced ZIKV replication. In OASL-IT1 knockout cells, the levels of interferons (IFNs) and the activation of 3 innate immune signaling pathways triggered by ZIKV were dramatically reduced. Collectively, our work found a positive feedback loop in the IFN system, in which IFNs and OASL-IT1 regulate each other, thereby promoting establishment of antiviral defense.
Keywords: Innate immunity; Interferon; Interferon-stimulated gene; Long noncoding RNA; Zika virus.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Type I Interferon Induction and Signaling: How Zika Virus Escapes from Host Innate Immunity.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 4;19(10):3015-3028. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.83056. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37416780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel IFNbeta-induced long non-coding RNA ZAP-IT1 interrupts Zika virus replication in A549 cells.Virol Sin. 2022 Dec;37(6):904-912. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.08.003. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Virol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35985476 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA Lnc-MxA Inhibits Beta Interferon Transcription by Forming RNA-DNA Triplexes at Its Promoter.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00786-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00786-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31434735 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Exerts Antihantaviral Effects by Acting as Positive Feedback for RIG-I Signaling.J Virol. 2017 Apr 13;91(9):e02250-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02250-16. Print 2017 May 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28202761 Free PMC article.
-
Evasion of Innate and Intrinsic Antiviral Pathways by the Zika Virus.Viruses. 2019 Oct 22;11(10):970. doi: 10.3390/v11100970. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31652496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zika virus infection in a cell culture model reflects the transcriptomic signatures in patients.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 25:2024.05.25.595842. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.25.595842. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 22;12(7):1499. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071499. PMID: 38826459 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Targeting Type I Interferon Induction and Signaling: How Zika Virus Escapes from Host Innate Immunity.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 4;19(10):3015-3028. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.83056. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37416780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC08148 promotes the caveola-mediated endocytosis of Zika virus through upregulating transcription of Src.J Virol. 2024 Jun 13;98(6):e0170523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01705-23. Epub 2024 May 14. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38742902 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Signatures of Zika Virus Infection in Patients and a Cell Culture Model.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 22;12(7):1499. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071499. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065267 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Regulatory Player in the Innate Immune System: Long Non-Coding RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 2;22(17):9535. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179535. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502451 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pierson TC, Diamond MS. The emergence of Zika virus and its new clinical syndromes. Nature. 2018 Aug;560((7720)):573–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

