BMI1 activates P-glycoprotein via transcription repression of miR-3682-3p and enhances chemoresistance of bladder cancer cell
- PMID: 34270461
- PMCID: PMC8351696
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203277
BMI1 activates P-glycoprotein via transcription repression of miR-3682-3p and enhances chemoresistance of bladder cancer cell
Abstract
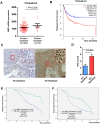
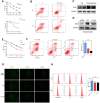
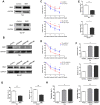
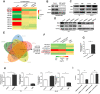
Chemoresistance is the most significant reason for the failure of cancer treatment following radical cystectomy. The response rate to the first-line chemotherapy of cisplatin and gemcitabine does not exceed 50%. In our previous research, elevated BMI1 (B-cell specific Moloney murine leukemia virus integration region 1) expression in bladder cancer conferred poor survival and was associated with chemoresistance. Herein, via analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas database and validation of clinical samples, BMI1 was elevated in patients with bladder cancer resistant to cisplatin and gemcitabine, which conferred tumor relapse and progression. Consistently, BMI1 was markedly increased in the established cisplatin- and gemcitabine-resistant T24 cells (T24/DDP&GEM). Functionally, BMI1 overexpression dramatically promoted drug efflux, enhanced viability and decreased apoptosis of bladder cancer cells upon treatment with cisplatin or gemcitabine, whereas BMI1 downregulation reversed this effect. Mechanically, upon interaction with p53, BMI1 was recruited on the promoter of miR-3682-3p gene concomitant with an increase in the mono-ubiquitination of histone H2A lysine 119, leading to transcription repression of miR-3682-3p gene followed by derepression of ABCB1 (ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1) gene. Moreover, suppression of P-glycoprotein by miR-3682-3p mimics or its inhibitor XR-9576, could significantly reverse chemoresistance of T24/DDP&GEM cells. These results provided a novel insight into a portion of the mechanism underlying BMI1-mediated chemoresistance in bladder cancer.
Keywords: BMI1; P-glycoprotein; bladder cancer; chemoresistance; miR-3682-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MDR1 mediated chemoresistance: BMI1 and TIP60 in action.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Aug;1859(8):983-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27295567 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead Box R2 Knockdown Decreases Chemoresistance to Cisplatin via MYC Pathway in Bladder Cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Nov 25;25:8928-8939. doi: 10.12659/MSM.917345. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31761897 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA UCA1 promotes cisplatin/gemcitabine resistance through CREB modulating miR-196a-5p in bladder cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2016 Nov 1;382(1):64-76. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.015. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27591936
-
Regulation of cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by epigenetic mechanisms.Drug Resist Updat. 2023 May;68:100938. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2023.100938. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Drug Resist Updat. 2023. PMID: 36774746 Review.
-
Pharmacogenomics in bladder cancer.Urol Oncol. 2014 Jan;32(1):16-22. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.09.007. Urol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24360659 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of miRNAs in Predicting Bladder Cancer Recurrence and Resistance to Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 4;24(2):964. doi: 10.3390/ijms24020964. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of proline-rich protein 11 as a major regulator in mouse spermatogonia maintenance via an increase in BMI1 protein stability.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Oct;49(10):9555-9564. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07846-8. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35980531
-
Activating transcription factor 5 (ATF5) promotes tumorigenic capability and activates the Wnt/b-catenin pathway in bladder cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Dec 11;21(1):660. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02315-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34895217 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Inhibition of O-Linked β-N-Acetylglucosamine Transferase as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy to Restore Chemosensitivity and Attenuate Aggressive Tumor Traits in Chemoresistant Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder.Biomedicines. 2022 May 18;10(5):1162. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051162. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625898 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Modifications and Non-Coding RNAs: Mutual Epigenetic Regulation and Role in Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 22;23(10):5801. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105801. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628612 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Bodrogi I, Albers P, Knuth A, Lippert CM, Kerbrat P, Sanchez Rovira P, Wersall P, et al.. Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic bladder cancer: results of a large, randomized, multinational, multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:3068–77. 10.1200/JCO.2000.18.17.3068 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grossman HB, Natale RB, Tangen CM, Speights VO, Vogelzang NJ, Trump DL, deVere White RW, Sarosdy MF, Wood DP Jr, Raghavan D, Crawford ED. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:859–66. 10.1056/NEJMoa022148 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jansen MP, Knijnenburg T, Reijm EA, Simon I, Kerkhoven R, Droog M, Velds A, van Laere S, Dirix L, Alexi X, Foekens JA, Wessels L, Linn SC, et al.. Hallmarks of aromatase inhibitor drug resistance revealed by epigenetic profiling in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013; 73:6632–41. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0704 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

