MicroRNA‑101 inhibits renal tubular epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition by targeting TGF‑β1 type I receptor
- PMID: 33955520
- PMCID: PMC8099196
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4952
MicroRNA‑101 inhibits renal tubular epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition by targeting TGF‑β1 type I receptor
Abstract
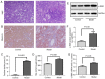
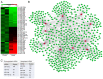
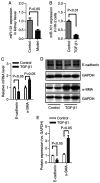
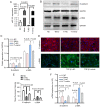
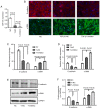
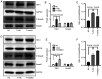
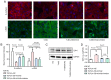
MicroRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) are key regulators of renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF). The present study was designed to identify miRNAs associated with the development of RIF, and to explore the ability of these identified miRNAs to modulate the renal tubular epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. To this end, miRNAs that were differentially expressed between normal and fibrotic kidneys in a rat model of mercury chloride (HgCl2)‑induced RIF were detected via an array‑based approach. Bioinformatics analyses revealed that miR‑101 was the miRNA that was most significantly downregulated in the fibrotic renal tissue samples, and this was confirmed by RT‑qPCR, which also demonstrated that this miRNA was downregulated in transforming growth factor (TGF)‑β1‑treated human proximal tubular epithelial (HK‑2) cells. When miR‑101 was overexpressed, this was sufficient to reverse TGF‑β1‑induced EMT in HK‑2 cells, leading to the upregulation of the epithelial marker, E‑cadherin, and the downregulation of the mesenchymal marker, α‑smooth muscle actin. By contrast, the downregulation of miR‑101 using an inhibitor exerted the opposite effect. The overexpression of miR‑101 also suppressed the expression of the miR‑101 target gene, TGF‑β1 type I receptor (TβR‑I), and thereby impaired TGF‑β1/Smad3 signaling, while the opposite was observed upon miR‑101 inhibition. To further confirm the ability of miR‑101 to modulate EMT, the HK‑2 cells were treated with the TβR‑I inhibitor, SB‑431542, which significantly suppressed TGF‑β1‑induced EMT in these cells. Notably, miR‑101 inhibition exerted a less pronounced effect upon EMT‑related phenotypes in these TβR‑I inhibitor‑treated HK‑2 cells, supporting a model wherein miR‑101 inhibits TGF‑β1‑induced EMT by suppressing TβR‑I expression. On the whole, the present study demonstrates that miR‑101 is capable of inhibiting TGF‑β1‑induced tubular EMT by targeting TβR‑I, suggesting that it may be an important regulator of RIF.
Keywords: TGF‑β1 type I receptor; microRNA‑101; renal interstitial fibrosis; tubular epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of BMP‑7 reverses TGF‑β1‑induced epithelial‑mesenchymal transition by attenuating the Wnt3/β‑catenin and TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathways in HK‑2 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Feb;21(2):833-841. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10875. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 31974602 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑152 regulates TGF‑β1‑induced epithelial‑mesenchymal transition by targeting HPIP in tubular epithelial cells.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jun;17(6):7973-7979. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8842. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29620271
-
miR-141 regulates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through repression of HIPK2 expression in renal tubular epithelial cells.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Feb;35(2):311-8. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.2008. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25421593 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of the lncRNA TUG1 attenuates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular epithelial cells by sponging miR-141-3p via regulating β-catenin.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):F1125-F1134. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00321.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33135476
-
Inhibition of miRNA‑135a‑5p ameliorates TGF‑β1‑induced human renal fibrosis by targeting SIRT1 in diabetic nephropathy.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Sep;46(3):1063-1073. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4647. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32705273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine Protects Against Kidney Fibrosis in Diabetic Mice by Targeting miR-101-3p-Mediated EndMT.Dose Response. 2022 Mar 30;20(1):15593258221083486. doi: 10.1177/15593258221083486. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. Dose Response. 2022. PMID: 35370507 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential for renal fibrosis by targeting Smad3-dependent noncoding RNAs.Mol Ther. 2024 Feb 7;32(2):313-324. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.12.009. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38093516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Circulating MicroRNAs (miR-21-5p, miR-20a-5p, miR-29b-3p, miR-126-3p and miR-101-3p) and Chronic Allograft Dysfunction in Renal Transplant Recipients.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 14;23(20):12253. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012253. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293110 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal‑miR‑1184 derived from mesenchymal stem cells alleviates cisplatin‑associated acute kidney injury.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):795. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12435. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34515319 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Exosomal Non-Coding RNA Profile Associated with Renal Damage Reveals Potential Therapeutic Targets in Lupus Nephritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 11;24(8):7088. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087088. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108249 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

