Screening of MicroRNA Related to Irradiation Response and the Regulation Mechanism of miRNA-96-5p in Rectal Cancer Cells
- PMID: 34458143
- PMCID: PMC8386172
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.699475
Screening of MicroRNA Related to Irradiation Response and the Regulation Mechanism of miRNA-96-5p in Rectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
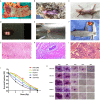
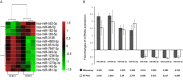
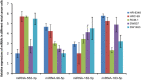
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy has been widely used in the treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer due to the excellent advantages of irradiation in cancer therapy. Unfortunately, not every patient can benefit from this treatment, therefore, it is of great significance to explore biomarkers that can predict irradiation sensitivity. In this study, we screened microRNAs (miRNAs) which were positively correlated with irradiation resistance and found that miRNA-552 and miRNA-183 families were positively correlated with the irradiation resistance of rectal cancer, and found that high expression of miRNA-96-5p enhanced the irradiation resistance of rectal cancer cells through direct regulation of the GPC3 gene and abnormal activation of the canonical Wnt signal transduction pathway. Based on the radioreactivity results of patient-derived xenograft models, this is the first screening report for radio-resistant biomarkers in rectal cancer. Our results suggest that miRNA-96-5p expression is an important factor affecting the radiation response of colorectal cancer cells.
Keywords: GPC3; Wnt/β-catenin; irradiation resistance; miRNA-96-5p; rectal cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Wu, Zhang, Yang, Zhou, Ren, Wang, Yang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of miR-21-5p as a predictive marker for complete tumor regression to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer patients.BMC Med Genomics. 2014 Dec 11;7:68. doi: 10.1186/s12920-014-0068-7. BMC Med Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25496125 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microRNAs Identified by Small RNA Sequencing as Potential Response Predictors in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Patients Treated With Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020 May-Jun;17(3):249-257. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20185. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32345666 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of biomarker microRNAs for predicting the response of colorectal cancer to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy based on microRNA regulatory network.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):2233-2248. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13659. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27903980 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA in rectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016 May 15;8(5):416-26. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v8.i5.416. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27190581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational Potential of MicroRNAs for Preoperative Staging and Prediction of Chemoradiotherapy Response in Rectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 12;11(10):1545. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101545. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31614848 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the radiotherapy-induced deferentially expressed RNAs in colorectal cancer management.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(12):1380-1389. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.71259.15482. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37970448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of non-coding RNAs in radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer: A narrative review.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 22;12:889658. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889658. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35936676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neoadjuvant treatment of rectal cancer: Where we are and where we are going.World J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 24;15(7):790-795. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v15.i7.790. World J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39071468 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Predictive Biomarkers in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy or Chemoradiotherapy: A Narrative Literature Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;15(5):1358. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051358. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crane CH, Skibber JM, Birnbaum EH, Feig BW, Singh AK, Delclos ME, et al. . The Addition of Continuous Infusion 5-FU to Preoperative Radiation Therapy Increases Tumor Response, Leading to Increased Sphincter Preservation in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2003) 57(1):84–9. 10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00532-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gentile M, Bucci L, Cerbone D, D'Antonio D, Guarino V. Evaluation of DOWNSTAGING as Leading Concept in Sphincter-Saving Surgery for Rectal Cancer After Preoperative Radio-Chemotherapy (Preop RCT). Ann Ital Chir (2003) 74(5):555–8. - PubMed
-
- Uzcudun AE, Batlle JF, Velasco JC, Sánchez Santos ME, Carpeño Jde C, Grande AG, et al. . Efficacy of Preoperative Radiation Therapy for Resectable Rectal Adenocarcinoma When Combined With Oral Tegafur-Uracil Modulated With Leucovorin: Results From a Phase II Study. Dis Colon Rectum (2002) 45(10):1349–58. 10.1007/s10350-004-6424-5 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

