Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 33468161
- PMCID: PMC7814551
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-020-02698-x
Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated bioinformatics analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated bioinformatics analysis.J Transl Med. 2021 Feb 11;19(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02728-2. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33573651 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a multisystemic, chronic inflammatory disease characterized by destructive systemic organ involvement, which could cause the decreased functional capacity, increased morbidity and mortality. Previous studies show that SLE is characterized by autoimmune, inflammatory processes, and tissue destruction. Some seriously-ill patients could develop into lupus nephritis. However, the cause and underlying molecular events of SLE needs to be further resolved.
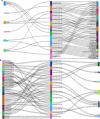
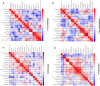
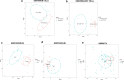
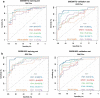
Methods: The expression profiles of GSE144390, GSE4588, GSE50772 and GSE81622 were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database to obtain differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between SLE and healthy samples. The gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichments of DEGs were performed by metascape etc. online analyses. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks of the DEGs were constructed by GENEMANIA software. We performed Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) to further understand the functions of the hub gene, Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) would be utilized to build a gene co-expression network, and the most significant module and hub genes was identified. CIBERSORT tools have facilitated the analysis of immune cell infiltration patterns of diseases. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were conducted to explore the value of DEGs for SLE diagnosis.
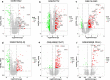
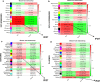
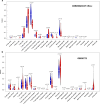
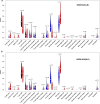
Results: In total, 6 DEGs (IFI27, IFI44, IFI44L, IFI6, EPSTI1 and OAS1) were screened, Biological functions analysis identified key related pathways, gene modules and co-expression networks in SLE. IFI27 may be closely correlated with the occurrence of SLE. We found that an increased infiltration of moncytes, while NK cells resting infiltrated less may be related to the occurrence of SLE.
Conclusion: IFI27 may be closely related pathogenesis of SLE, and represents a new candidate molecular marker of the occurrence and progression of SLE. Moreover immune cell infiltration plays important role in the progession of SLE.
Keywords: Biomarkers; IFI27; Immune infiltration; Integrated bioinformatics; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of EPSTI1 as a new potential biomarker for SLE based on GEO database.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 May;43(5):1531-1540. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06881-z. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38507132
-
Identification of Diagnostic Gene Markers and Immune Infiltration in Systemic Lupus.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 May 10;2022:3386999. doi: 10.1155/2022/3386999. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9862513. doi: 10.1155/2023/9862513. PMID: 35558576 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The shared circulating diagnostic biomarkers and molecular mechanisms of systemic lupus erythematosus and inflammatory bowel disease.Front Immunol. 2024 May 7;15:1354348. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354348. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38774864 Free PMC article.
-
PODN is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune infiltrates in osteosarcoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Jul 17;21(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02086-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34273970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone Involvement in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 22;23(10):5804. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105804. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and analysis of a disease risk prediction model for the systemic lupus erythematosus with random forest.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 1;13:1025688. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1025688. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405750 Free PMC article.
-
PANoptosis signaling enables broad immune response in psoriasis: From pathogenesis to new therapeutic strategies.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Nov 28;23:64-76. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.11.049. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 38125299 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNA-mRNA network and immune-related gene signatures in IgA nephropathy by integrated bioinformatics analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2021 Nov 25;22(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02606-5. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34823491 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Immune Cell Infiltration and Effective Diagnostic Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Bioinformatics Analysis.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 13;12:726747. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.726747. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484236 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic insights into superior grain number traits: a QTL analysis of wheat-Agropyron cristatum derivative pubing3228.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Apr 11;24(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04913-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38605289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Justiz Vaillant AA, Goyal A, Bansal P, Varacallo M: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). In StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2020, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

