NEIL3 may act as a potential prognostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 33879165
- PMCID: PMC8059184
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-01938-4
NEIL3 may act as a potential prognostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the leading cause of cancer-related death. This study aimed to develop and validate reliable prognostic biomarkers and signature.
Methods: Differentially expressed genes were identified based on three Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. Based on 1052 samples' data from our cohort, GEO and The Cancer Genome Atlas, we explored the relationship of clinicopathological features and NEIL3 expression to determine clinical effect of NEIL3 in LUAD. Western blotting (22 pairs of tumor and normal tissues), Real-time quantitative PCR (19 pairs of tumor and normal tissues), and immunohistochemical analyses (406-tumor tissues subjected to microarray) were conducted. TIMER and ImmuCellAI analyzed relationship between NEIL3 expression and the abundance of tumor-infiltrating immune cells in LUAD. The co-expressed-gene prognostic signature was established based on the Cox regression analysis.
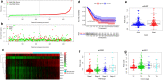
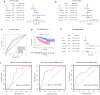
Results: This study identified 502 common differentially expressed genes and confirmed that NEIL3 was significantly overexpressed in LUAD samples (P < 0.001). Increased NEIL3 expression was related to advanced stage, larger tumor size and poor overall survival (p < 0.001) in three LUAD cohorts. The proportions of natural T regulatory cells and induced T regulatory cells increased in the high NEIL3 group, whereas those of B cells, Th17 cells and dendritic cells decreased. Gene set enrichment analysis indicated that NEIL3 may activate cell cycle progression and P53 signaling pathway, leading to poor outcomes. We identified nine prognosis-associated hub genes among 370 genes co-expressed with NEIL3. A 10-gene prognostic signature including NEIL3 and nine key co-expressed genes was constructed. Higher risk-score was correlated with more advanced stage, larger tumor size and worse outcome (p < 0.05). Finally, the signature was verified in test cohort (GSE50081) with superior diagnostic accuracy.
Conclusions: This study suggested that NEIL3 has the potential to be an immune-related therapeutic target and an independent predictor of LUAD prognosis. We also developed a prognostic signature for LUAD with a precise diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Immunohistochemistry; Lung adenocarcinoma; NEIL3; Prognostic signature; Real-time quantitative PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a robust immune-related prognostic signature in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma.J Transl Med. 2020 Oct 7;18(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02545-z. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33028329 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Immune Implication and Prognostic Value of IFI44L in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 3;11:798425. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.798425. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35047409 Free PMC article.
-
A signature of tumor DNA repair genes associated with the prognosis of surgically-resected lung adenocarcinoma.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 26;8:e10418. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10418. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33304656 Free PMC article.
-
AUNIP Expression Is Correlated With Immune Infiltration and Is a Candidate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Dec 9;10:590006. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.590006. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33363020 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature for Overall Survival Prediction in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 7;9:684259. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.684259. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34307361 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
DNA Damage Response Gene-Based Subtypes Associated With Clinical Outcomes in Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 22;9:901829. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.901829. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35813819 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics and Prognosis Analysis of N6-Methyladenosine Regulators in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Genet. 2021 Dec 9;12:746666. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.746666. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34956315 Free PMC article.
-
The nomogram for the prediction of overall survival in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma undergoing primary site surgery: A retrospective population-based study.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 15;12:916498. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.916498. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36033482 Free PMC article.
-
Standardized uptake valuemax of the primary lesion combined with tumor markers for clinically predicting distant metastasis in de novo lung adenocarcinoma.Cancer Med. 2024 Apr;13(7):e6961. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6961. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38549459 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram for cancer-specific survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients: A SEER based analysis.Surg Open Sci. 2024 Oct 18;22:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.sopen.2024.10.003. eCollection 2024 Dec. Surg Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 39525881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang L, Li L, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Sun J, Zhang X, Pan H, Liu S. SP1 induced long non-coding RNA LINC00958 overexpression facilitate cell proliferation, migration and invasion in lung adenocarcinoma via mediating miR-625-5p/CPSF7 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:24. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-1099-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeng X, Liu Q, Yang Y, Jia W, Li S, He D, Ma R. Placenta-specific protein 8 promotes the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma PC-9 cells and their tolerance to an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor by activating the ERK signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(5):5621–5627. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

