Extracellular vesicles from human umbilical cord blood plasma modulate interleukin-2 signaling of T cells to ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 32308765
- PMCID: PMC7163430
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.42742
Extracellular vesicles from human umbilical cord blood plasma modulate interleukin-2 signaling of T cells to ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
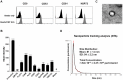
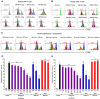
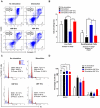
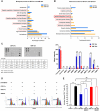
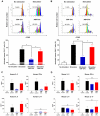
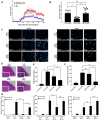
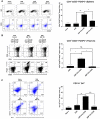
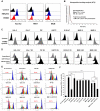
Human umbilical cord blood (UCB) cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EV) reportedly play immunosuppressive roles; however, UCB plasma-derived extracellular vesicles (CBP EVs) remain poorly studied. We examined the immunosuppressive potential of CBP EVs compared to that of adult blood plasma-derived extracellular vesicles (ABP EVs) in vitro and constructed an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model. Methods: CBP EVs were isolated by ultracentrifugation and their proteomic profiling was performed using the high-resolution liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Human T lymphocytes or mouse splenocytes labeled with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester were incubated with CBP EV to measure the immunosuppressive function of CBP EV. The effect on T-cell polarization was analyzed by flow cytometry and enzyme-linked immunospot assay. The matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) function in CBP EV was specifically inhibited using a chemical inhibitor. The efficacy of CBP EVs in the EAE mouse model was determined by scoring the symptoms and analyzing cell phenotype and cytokines using mouse splenocytes. We generated genetically engineered artificial EVs using HLA/MIC-null HEK293T (H1ME-5) cell line to characterize the immunosuppressive effect of CBP EV. Results: CBP EVs primarily inhibited the proliferation of T cells by reducing the production of IL-2. Specifically, CBP EV-derived matrix metallopeptidase cleaved the IL-2 receptor α (CD25) on the surface of activated T cells, consequently downregulating IL-2 signaling in response to IL-2R engagement. Although the inhibition of MMP activity in CBP EVs abrogated CD25 cleavage and restored IL-2 production in activated T cells, the immunosuppressive response was not fully recovered. Thus, we further analyzed changes in immunosuppressive cells such as regulatory T cells and bone marrow-derived suppressor cells by CBP EV. Further, GAL-3, GAL-7, S100-A7, MMP-9, MMP-8, HSP-72, and PIP were highly enriched in CBP EV-mimics in which they served as pivotal mediators of CBP EV-induced immunosuppressive effects. Therefore, we generated genetically engineered GAL-3, GAL-7, S100-A7, MMP-9, MMP-8, HSP-72, and PIP-EVs using HLA/MIC-null HEK293T cells to characterize the immunosuppressive effect of these molecules. Among these, MMP-9 and HSP-72-enriched EVs showed the most significant T cell immunosuppression. Conclusion: CBP EVs inhibited T cell proliferation and EAE development by modulating IL-2 signaling and immunosuppressive cell fate. CBP EVs contain critical components for immunosuppression and that CBP EV mimics, specifically those expressing MMP-9 and HSP-72, may offer a novel promising strategy for the treatment of various autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE); interleukin-2 (IL-2) signaling; matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9); regulatory T cell (Treg); umbilical cord blood plasma-derived extracellular vesicles (CBP EVs).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via regulating pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 2;11(1):11658. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91291-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34079033 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effects of extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Nov;235(11):8779-8790. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29721. Epub 2020 Apr 24. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32329062
-
Deferoxamine preconditioning of canine stem cell derived extracellular vesicles alleviates inflammation in an EAE mouse model through STAT3 regulation.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):19273. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68853-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39164295 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Mediators of Cellular Crosstalk Between Immune System and Kidney Graft.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 27;11:74. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00074. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32180768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles as a novel cell-free therapy for animal models of multiple sclerosis.Exp Neurol. 2024 Mar;373:114674. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114674. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38163474 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular vesicle-mediated heterogeneous communication between cancer and the lymphatic system facilitates lymphatic metastasis.Cancer Biol Med. 2023 Mar 24;20(3):174-80. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2023.0007. Cancer Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36971125 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lack of information about umbilical cord blood banking leads to decreased donation rates among Brazilian pregnant women.Cell Tissue Bank. 2021 Dec;22(4):597-607. doi: 10.1007/s10561-021-09903-1. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Cell Tissue Bank. 2021. PMID: 33576919
-
Identified GNGT1 and NMU as Combined Diagnosis Biomarker of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Utilizing Bioinformatics and Logistic Regression.Dis Markers. 2021 Jan 6;2021:6696198. doi: 10.1155/2021/6696198. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 33505535 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into optimizing exosome therapies for acute skin wound healing and other tissue repair.Front Med. 2024 Apr;18(2):258-284. doi: 10.1007/s11684-023-1031-9. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Front Med. 2024. PMID: 38216854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Truth Is Out There: Biological Features and Clinical Indications of Extracellular Vesicles from Human Perinatal Stem Cells.Cells. 2023 Sep 25;12(19):2347. doi: 10.3390/cells12192347. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Damien P, Allan DS. Regenerative Therapy and Immune Modulation Using Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Cells. Biol Blood Marrow Tr. 2015;21:1545–54. - PubMed
-
- Shkap V, Reske A, Pipano E, Fish L, Baszler T. Immunological relationship between Neospora caninum and Besnoitia besnoiti. Vet Parasitol. 2002;106:35–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

