Nonadherent culture method promotes MSC-mediated vascularization in myocardial infarction via miR-519d/VEGFA pathway
- PMID: 32616068
- PMCID: PMC7330937
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-01780-x
Nonadherent culture method promotes MSC-mediated vascularization in myocardial infarction via miR-519d/VEGFA pathway
Abstract
Background: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can provide therapeutic benefits for myocardial infarction (MI) recovery; however, the molecular mechanism by which MSCs improve the heart function is unclear.
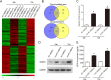
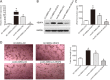
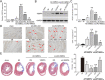
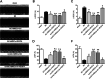
Methods: Microarray analysis was performed to examine the expression profiling of human MSCs (hMSCs) grown as adherent cultures (AC-hMSCs) or nonadherent cultures on ultra-low-adherent plates (nonAC-hMSCs). Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), western blotting, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) were used to assess VEGFA expression and secretion in the AC-hMSCs and nonAC-hMSCs. The paracrine effect of VEGFA-overexpressing AC-MSCs (AC-VEGFA-hMSCs) or VEGFA-knockdown nonAC-hMSCs (nonAC-shVEGFA-hMSCs) on the angiogenic ability of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) was evaluated using tube formation assay. AC-VEGFA-hMSCs or nonAC-shVEGFA-hMSCs were transplanted into myocardial infarction rats to investigate the therapeutic effect of AC-VEGFA-hMSCs or nonAC-shVEGFA-hMSCs. Luciferase reporter assay was used to confirm the association of VEGFA with miR-519d.
Results: Microarray analysis revealed that VEGFA is downregulated in AC-hMSCs compared to nonAC-hMSCs. Functional assays revealed that high levels of VEGFA produced from AC-VEGFA-hMSCs increased the tube formation capacity of HUVECs in vitro, improved angiogenesis and cardiac performance, and reduced infarct size in a rat MI model. Low levels of VEGFA secretion from nonAC-shVEGFA-hMSCs had the opposite effects. Mechanistically, we found that miR-519d directly targets VEGFA. High levels of VEGFA secreted from VEGFA-overexpressing nonAC-hMSCs abolished the repressive effect of miR-519d on HUVEC angiogenesis.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that nonadherent culture-induced secretion of VEGFA plays an important role in MSCs via the miR-519d/VEGFA pathway and may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for MI treatment.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Mesenchymal stem cells; Myocardial infarction; Nonadherent culture; VEGFA; miR-519d.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-377 regulates mesenchymal stem cell-induced angiogenesis in ischemic hearts by targeting VEGF.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 24;9(9):e104666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104666. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25251394 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA HOTAIR Protects Myocardial Infarction Rat by Sponging miR-519d-3p.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2019 Jun;12(3):171-183. doi: 10.1007/s12265-018-9839-4. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30607799
-
Circ-100290 Positively Regulates Angiogenesis Induced by Conditioned Medium of Human Amnion-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through miR-449a/eNOS and miR-449a/VEGFA Axes.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 May 18;16(12):2131-2144. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.39895. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549760 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles, via miR-210, improve infarcted cardiac function by promotion of angiogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Aug;1863(8):2085-2092. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.02.023. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28249798
-
miR-543 in human mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes cardiac microvascular endothelial cell angiogenesis after myocardial infarction through COL4A1.IUBMB Life. 2021 Jul;73(7):927-940. doi: 10.1002/iub.2474. Epub 2021 May 11. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 33890394
Cited by
-
Impact of Canine Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Conditioned Media on the Wound Healing Process: In Vitro and In Vivo Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 4;24(9):8214. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098214. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175924 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning the Microenvironment to Create Functionally Distinct Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Spheroids.Ann Biomed Eng. 2023 Jul;51(7):1558-1573. doi: 10.1007/s10439-023-03162-9. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Ann Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 36809393 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Signatures of Long Noncoding RNAs in Left Ventricular Noncompaction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 10;8:763858. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.763858. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34859074 Free PMC article.
-
From multi-omics approaches to personalized medicine in myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Oct 30;10:1250340. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1250340. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37965091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Empagliflozin-Pretreated Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Attenuated Heart Injury.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Feb 18;2023:7747727. doi: 10.1155/2023/7747727. eCollection 2023. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023. PMID: 36852325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang F, Zhu X, Hu XQ, Fang ZF, Tang L, Lu XL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with miR-126 release angiogenic factors and activate Notch ligand Delta-like-4, enhancing ischemic angiogenesis and cell survival. Int J Mol Med. 2013;31(2):484–492. - PubMed
-
- Wang N, Chen C, Yang D, Liao Q, Luo H, Wang X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles, via miR-210, improve infarcted cardiac function by promotion of angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. 2017;1863:2085–2092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

