LncRNA CSMD1-1 promotes the progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by activating MYC signaling
- PMID: 32685003
- PMCID: PMC7359090
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.45989
LncRNA CSMD1-1 promotes the progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by activating MYC signaling
Abstract
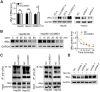
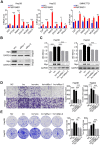
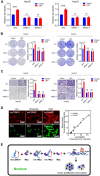
Emerging evidence suggests that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA) play critical roles in the development and progression of diverse cancers including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but the underlying molecular mechanisms of lncRNAs that are involved in hepatocarcinogenesis have not been fully explored. Methods: In this study, we profiled lncRNA expression in 127 pairs of HCC and nontumor liver tissues (a Discovery Cohort) using a custom microarray. The expression and clinical significance of lncCSMD1-1 were then validated with qRT-PCR and COX regression analysis in a Validation Cohort (n=260) and two External Validation Cohorts (n=92 and n=124, respectively). In vitro and in vivo assays were performed to explore the biological effects of lncCSMD1-1 on HCC cells. The interaction of lncCSMD1-1 with MYC was identified by RNA pull-down and RNA immunoprecipitation. The role of LncCSMD1-1 in the degradation of MYC protein was also investigated. Results: With microarray, we identified a highly upregulated lncRNA, lncCSMD1-1, which was associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in the Discovery Cohort, and validated in another 3 HCC cohorts. Consistently, ectopic expression of lncCSMD1-1 notably promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion, tumor growth and metastasis of HCC cells in in vitro and in vivo experiments. Gene expression profiling on HCC cells and gene sets enrichment analysis indicated that the MYC target gene set was significantly enriched in HCC cells overexpressing lncCSMD1-1, and lncCSMD1-1 was found to directly bind to MYC protein in the nucleus of HCC cells, which resulted in the elevation of MYC protein. Mechanistically, lncCSMD1-1 interacted with MYC protein to block its ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway, leading to activation of its downstream target genes. Conclusion: lncCSMD1-1 is upregulated in HCC and promotes progression of HCC by activating the MYC signaling pathway. These results provide the evidence that lncCSMD1-1 may serve as a novel prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Long noncoding RNA; MYC; lncCSMD1-1; prognosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA CPS1-IT1 suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating HIF-1α activity and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):43588-43603. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9635. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27248828 Free PMC article.
-
ID1 overexpression promotes HCC progression by amplifying the AURKA/Myc signaling pathway.Int J Oncol. 2020 Sep;57(3):845-857. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5092. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32705157
-
Six-long non-coding RNA signature predicts recurrence-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan 14;25(2):220-232. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i2.220. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30670911 Free PMC article.
-
Functional long non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2021 Mar 1;500:281-291. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.042. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33129957 Review.
-
Functional roles of lncRNA-TUG1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Life Sci. 2022 Nov 1;308:120974. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120974. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36126725 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Three-LncRNA Signature Predicting Tumor Recurrence in Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 20;12:754503. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.754503. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34745223 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-9-1 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis by Targeting UHRF1 in Lung Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211041191. doi: 10.1177/15330338211041191. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34520284 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms of LncRNAs Binding to Protein in Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 11;12(10):2925. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102925. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Diverse Role of CUB and Sushi Multiple Domains 1 (CSMD1) in Human Diseases.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 10;13(12):2332. doi: 10.3390/genes13122332. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Feb 14;17(1):253-265. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0418. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. Retraction in: Open Med (Wars). 2023 Dec 31;18(1):20230890. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0890. PMID: 35233463 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Pi J, Kang Y, Smith M, Earl M, Norigian Z, McBride A. A review in the treatment of oncologic emergencies. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2016;22:625–38. - PubMed
-
- Dang CV, Resar LM, Emison E, Kim S, Li Q, Prescott JE. et al. Function of the c-Myc oncogenic transcription factor. Exp Cell Res. 1999;253:63–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

