Human ESC-sEVs alleviate age-related bone loss by rejuvenating senescent bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 32944188
- PMCID: PMC7480439
- DOI: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1800971
Human ESC-sEVs alleviate age-related bone loss by rejuvenating senescent bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
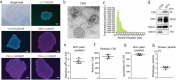
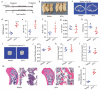
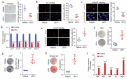
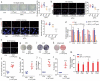
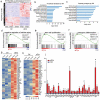
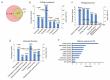
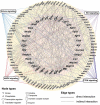
Tissue-resident stem cell senescence leads to stem cell exhaustion, which is a major cause of physiological and pathological ageing. Stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (SC-EVs) have been reported in preclinical studies to possess therapeutic potential for diverse diseases. However, whether SC-EVs can rejuvenate senescent tissue stem cells to prevent age-related disorders still remains unknown. Here, we show that chronic application of human embryonic stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles (hESC-sEVs) rescues the function of senescent bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and prevents age-related bone loss in ageing mice. Transcriptome analysis revealed that hESC-sEVs treatment upregulated the expression of genes involved in antiaging, stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in BM-MSCs. Furthermore, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis identified 4122 proteins encapsulated in hESC-sEVs. Bioinformatics analysis predicted that the protein components in the hESCs-sEVs function in a synergistic way to induce the activation of several canonical signalling pathways, including Wnt, Sirtuin, AMPK, PTEN signalling, which results in the upregulation of antiaging genes in BM-MSCs and then the recovery of senescent BM-MSCs function. Collectively, our findings reveal the effect of hESC-sEVs in reversing BM-MSCs senescence and age-related osteogenic dysfunction, thereby preventing age-related bone loss. Because hESC-sEVs could alleviate senescence of tissue-resident stem cells, they might be promising therapeutic candidates for age-related diseases.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicle; bone loss; bone marrow MSCs; cellular senescence; embryonic stem cells.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of The International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ESC-sEVs Rejuvenate Aging Hippocampal NSCs by Transferring SMADs to Regulate the MYT1-Egln3-Sirt1 Axis.Mol Ther. 2021 Jan 6;29(1):103-120. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.09.037. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33038325 Free PMC article.
-
Y-box binding protein 1 in small extracellular vesicles reduces mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to osteoblasts-implications for acute myeloid leukaemia.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Mar;13(3):e12417. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12417. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 38499475 Free PMC article.
-
Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-105-5p via small extracellular vesicles to rejuvenate senescent nucleus pulposus cells and attenuate intervertebral disc degeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 May 13;12(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02362-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33985571 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs delivered by small extracellular vesicles in MSCs as an emerging tool for bone regeneration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 31;11:1249860. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1249860. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37720323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles in the treatment of human diseases: Progress and prospect.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Jan 26;13(1):49-63. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i1.49. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33584979 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular senescence in metastatic prostate cancer: A therapeutic opportunity or challenge (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Sep;30(3):162. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13286. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38994760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intercellular mitochondrial transfer as a means of revitalizing injured glomerular endothelial cells.World J Stem Cells. 2022 Sep 26;14(9):729-743. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i9.729. World J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 36188114 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Therapeutic Properties Discovered with Extraordinary Success.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 10;9(6):667. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060667. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34200818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteopontin Rejuvenates Senescent Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Restores their Bone Tissue Regenerative Function.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 May;20(4):1106-1120. doi: 10.1007/s12015-024-10707-5. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 38472643 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of In Situ Grown Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles Modified Porous Polyetheretherketone Matrix Composites to Promote Osteointegration and Enhance Bone Repair.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 28;10:831288. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.831288. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35295654 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

