A novel mitochondrial amidoxime reducing component 2 is a favorable indicator of cancer and suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the expression of p27
- PMID: 32811980
- PMCID: PMC7498369
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-020-01417-6
A novel mitochondrial amidoxime reducing component 2 is a favorable indicator of cancer and suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the expression of p27
Abstract
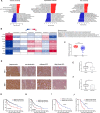
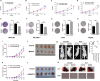
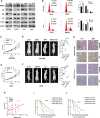
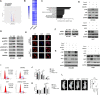
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality in the United States. Exploring the mechanism of HCC and identifying ideal targets is critical. In the present study, we demonstrated metabolism dysfunction might be a key diver for the development of HCC. The mitochondrial amidoxime reducing component 2 (MARC2) as a newly discovered molybdenum enzyme was downregulated in human HCC tissues and HCC cells. Downregulated MARC2 was significantly associated with clinicopathological characteristics of HCC, such as tumor size, AFP levels, and tumor grade and was an independent risk factor of poor prognosis. Both in vitro and in vivo studies suggested that MARC2 suppressed the progression of HCC by regulating the protein expression level of p27. The Hippo signaling pathway and RNF123 were required for this process. Moreover, MARC2 regulated expression of HNF4A via the Hippo signaling pathway. HNF4A was recruited to the promoter of MARC2 forming a feedback loop. MARC2 levels were downregulated by methylation. We demonstrated the prognostic value of MARC2 in HCC and determined the mechanism by which MARC2 suppressed the progression of HCC in this study. These findings may lead to new therapeutic targets for HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
WTAP facilitates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic silencing of ETS1.Mol Cancer. 2019 Aug 22;18(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1053-8. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31438961 Free PMC article.
-
NCAPG2 overexpression promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis through activating the STAT3 and NF-κB/miR-188-3p pathways.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jun;44:237-249. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.053. Epub 2019 Jun 5. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31176678 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-425-5p promotes invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through SCAI-mediated dysregulation of multiple signaling pathways.Oncotarget. 2017 May 9;8(19):31745-31757. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15958. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423650 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA alterations and mitochondrial dysfunction in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Dec 21;19(47):8880-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8880. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24379611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Metabolic Signatures in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2021 Jul 27;10(8):1901. doi: 10.3390/cells10081901. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440674 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in prognostic and therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: The hippo signaling pathway.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 12;12:937957. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.937957. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36033517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molybdenum's Role as an Essential Element in Enzymes Catabolizing Redox Reactions: A Review.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 19;14(7):869. doi: 10.3390/biom14070869. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) in tumorigenesis.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;12:1011230. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1011230. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36249028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting uridine-cytidine kinase 2 induced cell cycle arrest through dual mechanism and could improve the immune response of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Nov 26;27(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00403-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36447138 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of tissue proteomics in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma uncovers the underlying mechanism of lymph node metastasis and its significant sex disparities.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;12:887977. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.887977. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36106120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Chen D, Chen B. The long-to-short-axis ratio and multifocality are associated with TP53 mutation status in surgically resected hepatocellular carcinomas. Acad Radiol. 2018; e-pub ahead of print 27 June 2018; 10.1016/j.acra.2018.04.021. - PubMed
-
- Wahl B, Reichmann D, Niks D, Krompholz N, Havemeyer A, Clement B, et al. Biochemical and spectroscopic characterization of the human mitochondrial amidoxime reducing components hmARC-1 and hmARC-2 suggests the existence of a new molybdenum enzyme family in eukaryotes. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:37847–59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.169532. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

