KIAA1522 potentiates TNFα-NFκB signaling to antagonize platinum-based chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32854746
- PMCID: PMC7450600
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-020-01684-x
KIAA1522 potentiates TNFα-NFκB signaling to antagonize platinum-based chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: The platinum-based chemotherapy is the first-line regimen for the treatment of Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the therapeutic efficiency is largely limited by tenacious chemo-insensitivity that results in inferior prognosis in a cohort of patients. It has been known that KIAA1522 is aberrantly expressed and implicated in several types of solid tumors including NSCLC. Nowadays, knowledge about this gene is quite limited. Here, we aimed to identify the role of KIAA1522 in lung adenocarcinomas, and the molecular events that underlie KIAA1522-mediated chemoresistance to the platinum.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry were used to detect KIAA1522 expression in clinical NSCLC samples. Then, the survival analyses were performed to assess the link between KIAA1522 expression and overall survival or therapeutic outcome. In vivo depletion of KIAA1522 in adenocarcinoma cells were achieved by adeno-associated virus-mediated sgRNA/Cre delivery into the conditional KrasG12D/Cas9 expressed mice, which were designated to identify the roles of KIAA1522 in tumorigenesis and/or chemotherapy responses. The effects of KIAA1522 and downstream molecular events were studied by pharmacology in mice model and assays using in vitro cultured cells. The clinical relevance of our findings was examined by data-mining of online datasets from multiple cohorts.
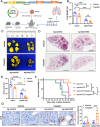
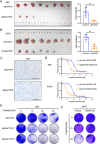
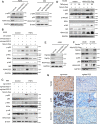
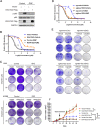
Results: The clinical evidences reveal that KIAA1522 independently predicts both the overall survival and the outcome of platinum-based chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinomas. By using a KrasG12D-driven murine lung adenocarcinoma model and performing in vitro assays, we demonstrated that KIAA1522 is a critical positive regulator of lung adenocarcinoma and a modulator of cisplatin response. KIAA1522 potentiates the TNFα-TNFR2-NFκB signaling which in turn intensifies recalcitrance to cisplatin treatment. These results were further manifested by integrative bioinformatic analyses of independent datasets, in which KIAA1522 is tightly associated with the activity of TNFα-NFκB pathway and the cisplatin-resistant gene signatures. More strikingly, overexpression of KIAA1522 counteracts the cisplatin-induced tumor growth arrest in vivo, and this effect can be remarkably diminished by the disruption of NFκB activity.
Conclusion: High expression of KIAA1522 is turned out to be an indicator of dismal effectiveness of platinum-based therapy in lung adenocarcinomas. KIAA1522 hyperactivates TNFα-NFκB signaling to facilitate resistance to platinum reagents. Targeting NFκB signaling through small molecule inhibitors may be a rational strategy to conquer chemoresistance and synergize platinum-based chemotherapy in KIAA1522 overexpressed lung adenocarcinomas.
Keywords: Chemoresistance; KIAA1522; Lung adenocarcinoma; NFκB; Platinum-based chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation of lung cancer cell plasticity and heterogeneity with the restoration of cisplatin sensitivity by neurotensin antibody.Cancer Lett. 2019 Mar 1;444:147-161. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30583074
-
Exosomal miR-4443 promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung carcinoma by regulating FSP1 m6A modification-mediated ferroptosis.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 1;276:119399. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119399. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33781830
-
Aurora-A/NF-ĸB Signaling Is Associated With Radio-resistance in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2019 Nov;39(11):5991-5998. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13804. Anticancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31704824
-
Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategy in platinum resistance lung cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Aug;1876(1):188577. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188577. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34098035 Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Chemoresistance Induced by Cisplatin in NSCLC Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 18;22(16):8885. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168885. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ferroptosis-related genes DUOX1 and HSD17B11 affect tumor microenvironment and predict overall survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 31;103(22):e38322. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038322. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39259123 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic Significance of KIAA1522 Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients.Cureus. 2023 Aug 24;15(8):e44016. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44016. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37746394 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Modeling of Lung Adenocarcinoma Based on Hypoxia and Ferroptosis-Related Genes.J Oncol. 2022 Sep 19;2022:1022580. doi: 10.1155/2022/1022580. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36245988 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive adverse effects of chemotherapy and immunotherapy: are interventions within reach?Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Mar;18(3):173-185. doi: 10.1038/s41582-021-00617-2. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35140379 Review.
-
Prognostic and immune implications of a novel ferroptosis-related ten-gene signature in lung adenocarcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jul;9(13):1058. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-7936. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34422970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553(7689):446–454. - PubMed
-
- Li XT, Yang JJ, Wu YL, Hou J. Toward innovative combinational immunotherapy: a systems biology perspective. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;68:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Eberhardt WE, et al. The IASLC lung Cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(1):39–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

