An R2R3 MYB transcription factor confers brown planthopper resistance by regulating the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase pathway in rice
- PMID: 31848246
- PMCID: PMC6955232
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1902771116
An R2R3 MYB transcription factor confers brown planthopper resistance by regulating the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase pathway in rice
Abstract
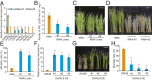
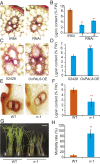
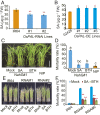
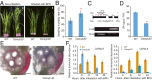
Brown planthopper (BPH) is one of the most destructive insects affecting rice (Oryza sativa L.) production. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) is a key enzyme involved in plant defense against pathogens, but the role of PAL in insect resistance is still poorly understood. Here we show that expression of the majority of PALs in rice is significantly induced by BPH feeding. Knockdown of OsPALs significantly reduces BPH resistance, whereas overexpression of OsPAL8 in a susceptible rice cultivar significantly enhances its BPH resistance. We found that OsPALs mediate resistance to BPH by regulating the biosynthesis and accumulation of salicylic acid and lignin. Furthermore, we show that expression of OsPAL6 and OsPAL8 in response to BPH attack is directly up-regulated by OsMYB30, an R2R3 MYB transcription factor. Taken together, our results demonstrate that the phenylpropanoid pathway plays an important role in BPH resistance response, and provide valuable targets for genetic improvement of BPH resistance in rice.
Keywords: brown planthopper; lignin; phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; rice; salicylic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Revealing different systems responses to brown planthopper infestation for pest susceptible and resistant rice plants with the combined metabonomic and gene-expression analysis.J Proteome Res. 2010 Dec 3;9(12):6774-85. doi: 10.1021/pr100970q. Epub 2010 Nov 1. J Proteome Res. 2010. PMID: 20936879
-
Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Dec 29;106(52):22163-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912139106. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 20018701 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of transcription factors potential related to brown planthopper resistance in rice via microarray expression profiling.BMC Genomics. 2012 Dec 10;13:687. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-687. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23228240 Free PMC article.
-
Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper.Mol Plant. 2013 May;6(3):621-34. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst030. Epub 2013 Feb 9. Mol Plant. 2013. PMID: 23396040 Review.
-
Evolving ideas about genetics underlying insect virulence to plant resistance in rice-brown planthopper interactions.J Insect Physiol. 2016 Jan;84:32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 5. J Insect Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26668110 Review.
Cited by
-
Necessity of rice resistance to planthoppers for OsEXO70H3 regulating SAMSL excretion and lignin deposition in cell walls.New Phytol. 2022 May;234(3):1031-1046. doi: 10.1111/nph.18012. Epub 2022 Feb 26. New Phytol. 2022. PMID: 35119102 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and Transcriptomic Profiling of Lilium Leaves Infected With Botrytis elliptica Reveals Different Stages of Plant Defense Mechanisms.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Sep 22;12:730620. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.730620. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34630478 Free PMC article.
-
Phloem unloading via the apoplastic pathway is essential for shoot distribution of root-synthesized cytokinins.Plant Physiol. 2021 Aug 3;186(4):2111-2123. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab188. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33905524 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive evaluation of Chinese peanut mini-mini core collection and QTL mapping for aflatoxin resistance.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Apr 21;22(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03582-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35448951 Free PMC article.
-
IbMYB308, a Sweet Potato R2R3-MYB Gene, Improves Salt Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;13(8):1476. doi: 10.3390/genes13081476. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rivera C. T., Ou S. H., Lida T. T., Grassy stunt disease of rice and its transmission by Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Plant Dis. Rep. 50, 453–456 (1966).
-
- Ling K. C., Tiongco E. R., Aguiero V. M., Rice ragged stunt, a new virus disease. Plant Dis. Rep. 62, 701–705 (1978).
-
- Liu Y., et al. , A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 301–305 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

